
Introduction
Standard deviation is a crucial concept in statistics, and it plays an especially important role in the stock market. As an investor, understanding how to calculate standard deviation and what it signifies can give you significant insights into the level of risk and volatility associated with different investments. In this blog, we’ll dive into what standard deviation is, how to calculate it, and how it is applied in the stock market to measure risk and predict market behavior. We’ll also explore various examples and scenarios to help you grasp how they can be used to your advantage in making informed financial decisions.
Standard Deviation in the Stock Market
Overview of Standard Deviation
Standard deviation is a measure of the spread or dispersion of a set of data points. In the stock market, it helps investors understand how much a stock’s price deviates from its average or expected price over a given period. A higher standard deviation indicates greater volatility, meaning the stock’s price is more spread out from the average. Conversely, a lower standard deviation suggests less volatility, implying the stock price stays closer to the average price.
Importance in Stock Market Analysis
It is essential for investors because it provides an objective measure of risk. By calculating standard deviation, you can determine how much a stock’s price tends to fluctuate within a specific time frame. This information is crucial when making investment decisions because it helps you evaluate the potential risk and reward of a stock, which is vital when building a portfolio or planning your next trade.
What is Standard Deviation?
Definition and Concept
In statistical terms, the standard deviations are the square root of the variance. Variance itself measures how far each data point in a data set is from the mean (average) and, thus, how spread out the values are. Standard deviation, then, takes that variance and brings it back to the original unit of measurement, making it more interpretable.
In the context of the stock market, the “data points” are the stock’s daily, weekly, or monthly prices (depending on the time frame you are analyzing). The standard deviations help to quantify how much the stock price deviates from the expected price, which can help predict future price movement and assess the risk of holding that stock.
Understanding the Role of Standard Deviation in Finance
The standard deviation in finance is often used to measure the risk of an asset. The higher the standard deviations, the higher the volatility, and therefore, the higher the potential risk. When investors use standard deviation, they can make decisions based on the level of risk they are willing to take. Additionally, standard deviations are useful for constructing diversified portfolios, where the goal is to balance high and low-risk assets.
Statistics Standard Deviation: Key Concepts
Relation to Risk and Volatility
In the context of financial markets, volatility refers to the extent to which the price of a security or asset fluctuates over time. It is essentially a measure of the unpredictability or risk associated with the asset’s price movements. Higher volatility indicates that the price of the asset is subject to larger swings, while lower volatility suggests more stable or predictable price behavior.
One of the most effective ways to quantify volatility in the stock market is through standard deviations. Standard deviation measures how much the price of a stock deviates, or varies, from its average price over a given period of time. This provides investors with an idea of the degree of risk involved in holding a particular stock.
The relationship between standard deviation and volatility can be summarized as follows:
- A high standard deviation means the stock’s price fluctuates widely from the average price, which signifies greater volatility and, hence, higher risk. In this case, the stock’s future price movements are less predictable, and the investor is likely exposed to greater uncertainty.
- A low standard deviation indicates that the stock’s price is more stable and does not deviate significantly from the average price. This implies lower volatility and lower risk, making the stock a more predictable and safer investment in terms of price fluctuations.
For example, if a stock’s price fluctuates between $95 and $110 over a month, with an average of $100, a higher standard deviation would mean that the stock price regularly moves further away from the $100 mark indicating that its movements are more volatile and unpredictable. Conversely, a lower standard deviation would indicate that the stock price stays closer to the average, making it a more stable investment.
Measuring Price Fluctuations in Stocks
Standard deviations are versatile in that they can be applied over different time frames to gauge price fluctuations. The most common time frames used for calculating standard deviation in the stock market are daily, weekly, or monthly periods. The purpose of using standard deviations in this way is to understand how much a stock’s price deviates from its average price over the selected period, which can then be used to assess its risk.
Daily Price Movements:
If you are looking at daily price movements, you would calculate the standard deviations of the daily closing prices. This approach provides a short-term view of volatility and is especially useful for day traders or short-term investors who need to understand the price fluctuations of a stock daily. A stock with higher daily standard deviations would suggest that there are substantial intraday price swings, which could either present opportunities or risks depending on the trader’s strategy.
Monthly Returns:
For long-term investors, calculating the standard deviation of monthly returns may be more relevant. In this case, you’re looking at the broader fluctuations of the stock price over an extended period, which can give you a more comprehensive view of the asset’s risk profile. Investors who are focused on long-term growth or stability typically prefer stocks with a lower monthly standard deviation, as it implies less price volatility and greater predictability in the longer term.
For example, if an investor is analyzing a stock’s monthly returns, they would calculate the standard deviation of those returns over the past several months. Higher standard deviations of returns would suggest that the stock has had large price swings between months, which could indicate a higher risk. On the other hand, a lower standard deviation would suggest that the stock’s returns have been more stable and predictable over time.
Practical Example of Standard Deviation in Price Fluctuations
Let’s say an investor is considering two stocks, Stock A and Stock B. Over the past month:
- Stock A has had daily price fluctuations ranging from $50 to $60, with an average price of $55.
- Stock B has had daily price fluctuations ranging from $53 to $57, with an average price of $55.
Stock A has a much higher standard deviation than Stock B, which means that Stock A is more volatile and has larger price swings. Stock B, on the other hand, has a smaller standard deviation, making it less volatile and more predictable in terms of price movements.
The investor, depending on their risk tolerance, may choose Stock A if they are looking for higher potential returns (accepting the higher volatility), or Stock B if they prefer a more stable and predictable investment.
Significance in Investment Strategy
Understanding how to measure and interpret standard deviation can help investors in making better decisions regarding portfolio construction. Investors can use standard deviation to assess the overall risk level of their portfolio. A portfolio that includes stocks with high standard deviations will likely have higher potential returns but will also come with higher risk. Conversely, a portfolio made up of stocks with low standard deviations will tend to have less risk but may also provide lower returns.
Investors can also use standard deviation in conjunction with other statistical measures like the mean (average return) and Sharpe ratio to evaluate the risk-adjusted returns of their portfolio. The Sharpe ratio, for example, is calculated by dividing the difference between the portfolio return and the risk-free rate by the standard deviation of the portfolio’s returns. This ratio helps investors assess how well the return of an asset compensates them for the risk they are taking.
By analyzing standard deviation, investors can make data-driven decisions and develop a strategy that aligns with their risk tolerance and investment goals, whether they are looking for short-term trading opportunities or long-term growth.
How to Calculate Standard Deviation
Step-by-Step Guide on Calculation
Calculating standard deviation may seem intimidating at first, but once you understand the formula and the steps involved, it becomes a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculate standard deviation:
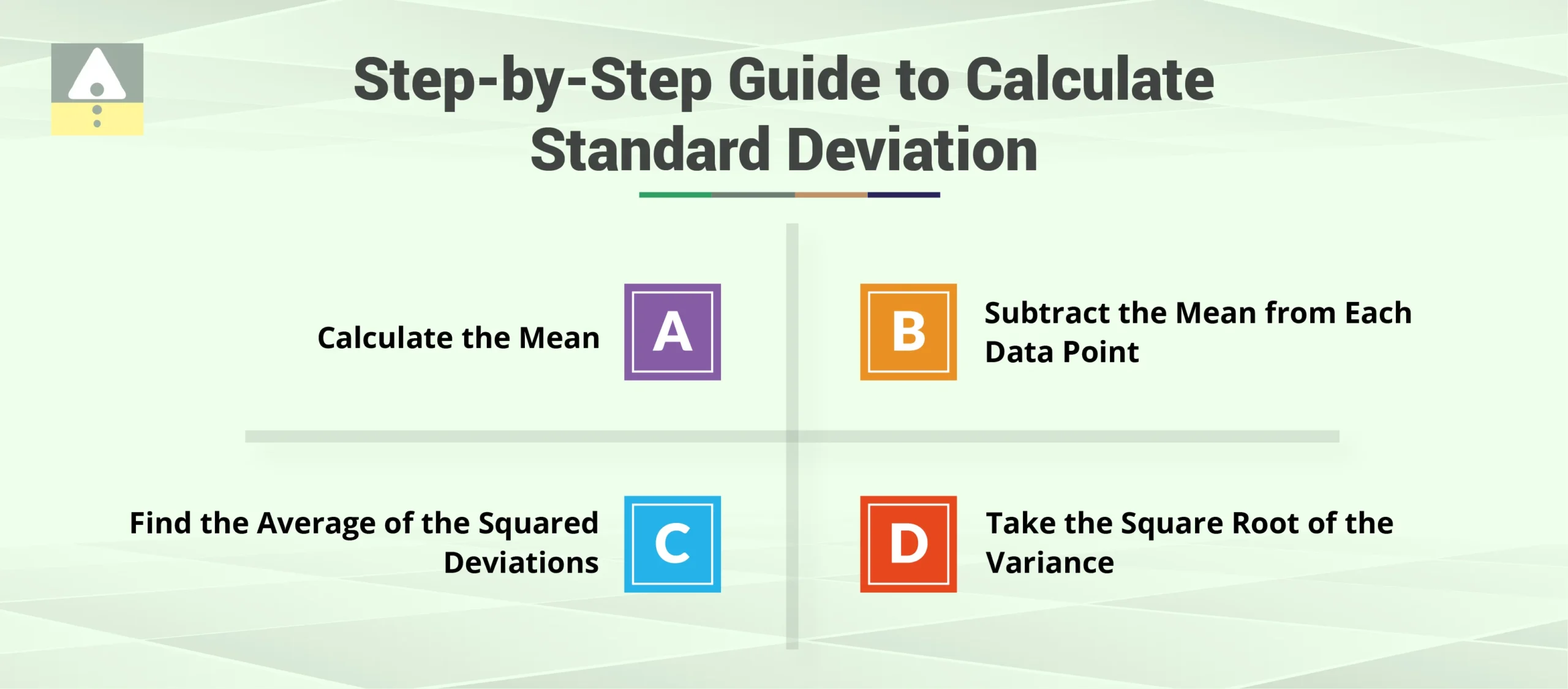
- Calculate the Mean: First, you need to calculate the mean (average) of the data points (prices). The formula for the mean is:
∑X / N
∑X is the sum of all data points, and N is the number of data points. - Subtract the Mean from Each Data Point: For each data point, subtract the mean and square the result. This will give you the squared deviations.
- Find the Average of the Squared Deviations: Now, calculate the average of these squared deviations. This step is called calculating the variance.
Variance=∑(Xi−μ)2 / N
Where XiX_iXi represents each data point, and μmuμ is the mean. - Take the Square Root of the Variance: The final step is to take the square root of the variance, which gives you the standard deviation.
Standard Deviation= Square root of Variance
Tools and Methods Used
While the manual calculation method helps understand the concept, most traders and investors use financial software or online tools to calculate standard deviation automatically. Tools like Excel, Google Sheets, or specific stock analysis software can compute the standard deviation for you with just a few clicks.
Standard Deviation Formula
Detailed Explanation of the Formula
The formula for calculating standard deviation can be written as:
σ= ∑(Xi−μ)2 / N
Where:
- σsigmaσ is the standard deviation
- XiX_iXi represents each data point (i.e., daily stock prices)
- μmuμ is the mean (average) of the data points
- NNN is the number of data points (i.e., the total number of days or periods)
This formula calculates the average deviation from the mean, allowing investors to gauge how volatile a stock’s price might be.
Standard Deviation Equation
Breaking Down the Equation
The equation for standard deviation includes two major components:
- Squared Differences: (Xi−μ)2 represents the squared difference between each data point and the mean. This is essential because it ensures that both positive and negative deviations from the mean are treated equally.
- Averaging: By dividing the sum of squared deviations by the number of data points, you get the variance, which gives a general sense of how spread out the data points are.
Finally, by taking the square root of the variance, you return the measure to the original unit of measurement, allowing it to be more interpretable in practical terms, such as stock prices.
Standard Deviation Calculation in the Stock Market
Calculating for Stock Returns
To calculate the standard deviation for stock returns, you would follow these steps:
- Collect Historical Data: Gather the daily or monthly closing prices of the stock you’re analyzing.
- Calculate Daily Returns: Subtract the previous day’s closing price from the current day’s closing price, then divide by the previous day’s closing price. This gives you a daily return.
- Calculate the Standard Deviation of Returns: Use the formula to calculate the standard deviation of these daily returns. The result will tell you how volatile the stock’s returns are over the period you’ve analyzed.
Examples of Standard Deviation Calculation
Let’s say you have a stock with the following closing prices for the past five days: $100, $105, $110, $95, $102. To calculate the standard deviations:
- Find the Mean: 100+105+110+95+1025=102.4frac100 + 105 + 110 + 95 + 1025 = 102.45100+105+110+95+102=102.4
- Find the Squared Differences from the Mean:
- (100−102.4)2=5.76(100 – 102.4)^2 = 5.76(100−102.4)2=5.76
- (105−102.4)2=6.76(105 – 102.4)^2 = 6.76(105−102.4)2=6.76
- (110−102.4)2=57.76(110 – 102.4)^2 = 57.76(110−102.4)2=57.76
- (95−102.4)2=54.76(95 – 102.4)^2 = 54.76(95−102.4)2=54.76
- (102−102.4)2=0.16(102 – 102.4)^2 = 0.16(102−102.4)2=0.16
- Find the Variance: 5.76+6.76+57.76+54.76+0.165=25.04frac5.76 + 6.76 + 57.76 + 54.76 + 0.165 = 25.0455.76+6.76+57.76+54.76+0.16=25.04
- Find the Standard Deviations: 25.04≈5.0sqrt25.04 approx 5.025.04≈5.0
The standard deviation of this stock’s price movement is 5.0, indicating a moderate level of volatility.
Deviation in Statistics and Its Impact
Understanding Deviation in Statistical Terms
In statistics, deviation refers to the difference between a data point and the mean. The greater the deviation, the farther the data point is from the average. In the stock market, large deviations from the average stock price could indicate significant volatility or potential profit opportunities.
How Deviation Relates to Stock Market Movements
Deviation statistics help investors gauge how unusual a stock’s price movement is compared to its historical price trend. A higher deviation indicates greater unpredictability, which may suggest higher risk. Conversely, smaller deviations could signal a more stable market environment, which may be more appealing for risk-averse investors.
Standard Deviations Example in Finance
Real-life Examples of Standard Deviations in Stock Market Movements
Let’s look at some examples of how standard deviations can be applied in finance:
- Volatile Stocks: If a stock like Tesla has high standard deviations, its price is likely to fluctuate significantly within a short period. For example, Tesla might experience 5-10% swings in price in a day, making it a high-risk investment.
- Stable Stocks: A utility stock, such as Duke Energy, might have a lower standard deviation because its price is less likely to fluctuate dramatically. Investors who prioritize stability over high returns might prefer such stocks.
Interpretation of Results from Stock Data
Understanding the standard deviation of a stock allows investors to determine whether the stock fits within their risk tolerance. A stock with higher standard deviations may offer higher potential returns, but it also comes with greater risks. Conversely, lower standard deviation stocks offer lower risks but may not provide as much growth potential.
Deviation Statistics: How It Affects Investor Decision-making
The Role of Deviation in Portfolio Management
Investors use deviation statistics when deciding how to allocate assets in a portfolio. By choosing assets with different levels of deviation, investors can create a diversified portfolio that balances risk and return. For example, combining high-deviation stocks (like tech stocks) with low-deviation stocks (like utility stocks) can reduce overall portfolio risk.
Predicting Stock Volatility Using Deviation
By analyzing the standard deviations of a stock’s past price movements, investors can get a better understanding of how volatile the stock might be in the future. This helps investors make more informed decisions about whether to hold, buy, or sell a stock based on their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Open free demat account in 5 minutes
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the concept of standard deviations and how to calculate standard deviations is crucial for anyone looking to make informed decisions in the stock market. This statistical measure not only helps investors gauge the volatility and risk of individual stocks but also aids in portfolio management. By learning how to interpret standard deviation examples and apply the deviation formula, investors can better assess the potential price movements of their investments.
For those interested in making data-driven investment decisions, Jainam Broking Ltd. offers expert research and tools to help you analyze market risks and develop a strategy that aligns with your financial goals. Whether you’re looking to assess standard deviation statistics or exploring various investment opportunities, Jainam Broking Ltd. is here to empower traders and investors with the knowledge and resources they need to succeed in the dynamic stock market.
Are you planning on trading in the stock market? If yes, you are at the right place!
Open a Free Demat Account with Jainam Broking Ltd. Now!
publish_date]








